ScienceDaily (Feb. 28, 2012) — We know since the dawn of modern physics that although events in our everyday life can be described by classical physics, the interaction of light and matter is down deep governed by the laws of quantum mechanics. Despite this century-old wisdom, accessing truly quantum mechanical situations remains nontrivial, fascinating and noteworthy even in the laboratory. Recently, interest in this area has been boosted beyond academic curiosity because of the potential for more efficient and novel forms of information processing.
Alister's SoftMachine outfit is a morphing, colour changing outfit that receives instructions from both Alister and the world's most powerful supercomputer. The wireless function is built into the nanomaterial of the outfit.
Here's a rehash exercise I undertook of the Science Daily article just to help me understand what had been achieved
"A single atom or molecule acts as a quantum bit processing signals delivered via single photons.
It is possible to set up a situation where single molecules can be detected and single photons generated.
The problem is putting together a simple one on one interaction because billions of photons per second are usually impinged on a molecule to obtain a signal from it.
First off, you would have to find a suitable source of single photons, which have the proper frequency and bandwidth. Although lasers come in different colours and specifications, something that fires single photons can't be bought at Maplins or Radio Shack
One common way to get around this difficulty in atomic physics is to build a cavity around the atom so that a photon remains trapped for long enough times to increase the chances of a 1-1 interaction.
And it's been done. Connecting a single flying photon with a single molecule.
So a team of scientists (at ETH Zurich and Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light in Erlangen) led by Professor Vahid Sandoghdar made something that spits out single photons.
How? Well they cheated a little by using a photon release event that happens naturally. When an atom or molecule absorbs a photon it makes a transition to a so-called excited state. After a few nanoseconds (one thousand millionth of a second) this state decays to its initial ground state and emits exactly one photon.
So the group used two samples of fluorescent molecules embedded in organic crystals and cooled them to about 1.5 K (-272 °C). Single molecules in each sample were detected by a combination of spectral and spatial selection.
To generate single photons, a single molecule was excited in the “source” sample and when the excited state of the molecule decayed, the emitted photons were collected and tightly focused onto the “target” sample at a distance of a few meters.
The team had to (1) make sure the photon and the molecule had the same frequency; and (2) get the single photons to interact with the target molecule in an efficient manner.
Not that easy when the focus of a light beam cannot be smaller than a few hundred nanometers; while a molecule is about one nanometer in size (100,000 times smaller than the diameter of a human hair); which would lead to most of the incoming light (photons) going around the molecule, i.e. without them seeing each other.
Here's the 'but'; if the incoming photons are resonant with the quantum mechanical transition of the molecule, the molecule acts more like a prefect little catchers glove to the area of the focused light and grabs the light waves in its vicinity.
The experimental work was performed at ETH Zurich before the group of Prof. Sandoghdar moved to the newly founded Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light in Erlangen in 2011."
I write Scifi. I've moved the blog to http://www.softmachine.net You'll find all the new stuff there @NathanMcGrathSF. Nathan.
Wednesday 29 February 2012
Wi-fi on an atomic scale - the perfect fit
IBM close to Working Quantum Computer
Monday 27 February 2012
Free Links to Increase your browsing privacy
Increase your browsing privacy
On March 1st, Google will implement its new, unified privacy policy, which will affect data Google has collected on you prior to March 1st as well as data it collects on you in the future. Earlier this week, we showed you how to delete your Google Web History in order to prevent Google from combining your Web History data with the data it has about you on its other products to provide you with personalized ads or suggestions across all of its products. You may also wish to delete your YouTube Viewing and Search History, which can reveal particularly sensitive information about you, including your location, interests, age, sexual orientation, religion, and health concerns.
On March 1st, Google will implement its new, unified privacy policy, which will affect data Google has collected on you prior to March 1st as well as data it collects on you in the future. Earlier this week, we showed you how to delete your Google Web History in order to prevent Google from combining your Web History data with the data it has about you on its other products to provide you with personalized ads or suggestions across all of its products. You may also wish to delete your YouTube Viewing and Search History, which can reveal particularly sensitive information about you, including your location, interests, age, sexual orientation, religion, and health concerns.
The Electronic Frontier Foundation has produced some invaluable yet simple guides on steps you can take to increase your privacy when browsing the web; not just from Google but all the other corporate residents that make use of the data they gather on your browsing activity.
The Link Here provides more help
Ever asked yourself 'What is Matter?'
Saturday 25 February 2012
Nanomaterials and the 'do anything you want' outfit.
ScienceDaily (Feb. 24, 2012) — Researchers at the NanoScience Center of the University of Jyväskylä, Finland, and at Harvard University, US, have discovered a novel way to make nanomaterials. Computer simulations predict that long and narrow graphene nanoribbons can be rolled into carbon nanotubes by means of twisting. Being classical in origin, the mechanism is robust and valid on the macro-, micro- and nanoscale.
The mechanism also enables experimental control, which has earlier been impossible. The mechanism can be used to make various kinds of novel carbon nanotubes, to encapsulate molecules insides the tubes, or to make tubules from ribbons made out of other planar nanomaterials.
For the past twenty years, carbon nanotubes have been described as "rolled-up graphenes," even though no-one ever really did the rolling. Today, nanotubes, along with many other nanomaterials, are made by atom-by-atom growth.
The results were published in Physical Review B. The research used the computer resources of the Finnish IT Centre for Science (CSC), based in Espoo.
Part Two.
Add to this a couple of other developments reported here in the blog. (a) atom sized transistors and (b) technologies powered by touch and, boom: a computer woven into the nanomaterials of your clothing and powered by the kinetic and thermal energy produced by your movement.
Elsewhere here you'll find posts on brain-machine interfaces. It is feasible to consider a material containing nanotechnology components with different functions; one of which will be to allow manipulation of the different technologies in the outfit by thought alone.
The mechanism also enables experimental control, which has earlier been impossible. The mechanism can be used to make various kinds of novel carbon nanotubes, to encapsulate molecules insides the tubes, or to make tubules from ribbons made out of other planar nanomaterials.
For the past twenty years, carbon nanotubes have been described as "rolled-up graphenes," even though no-one ever really did the rolling. Today, nanotubes, along with many other nanomaterials, are made by atom-by-atom growth.
The results were published in Physical Review B. The research used the computer resources of the Finnish IT Centre for Science (CSC), based in Espoo.
Part Two.
Add to this a couple of other developments reported here in the blog. (a) atom sized transistors and (b) technologies powered by touch and, boom: a computer woven into the nanomaterials of your clothing and powered by the kinetic and thermal energy produced by your movement.
Elsewhere here you'll find posts on brain-machine interfaces. It is feasible to consider a material containing nanotechnology components with different functions; one of which will be to allow manipulation of the different technologies in the outfit by thought alone.
Thursday 23 February 2012
Nanotechnology, neuroscience, bye bye free will..
In June 2009. Honda came up with a new Brain-Machine Interface helmet that gave the user power to communicate telepathically with humanoids. It reads your thoughts by measuring changes in electrical current and blood flow in the brain.
Things have moved on from then. Developments in nanotechnology means that data can now flow in two directions.
take the New Scientist article (reported in io9): " For the first time ever, scientists can control human brain cells using quantum dots
What if you could treat conditions ranging from Alzheimer's to blindness, all with a flash of light? Researchers think it's possible — and they plan on using tiny particles called quantum dots to do it.
Brain stimulation can be incredibly tricky. Performing it from outside the head is effective, but doesn't give you very much specificity when it comes to turning on a specific brain region...Recently, researchers have sought out solutions to these problems with methods that rely on light, in hopes that they can be used to stimulate brain activity with a high level of precision without having to crack your skull open. Right now, the buzz-word in light-mediated brain stimulation is optogenetics, which looks incredibly promising, but relies on genetic modifications that are still considered too risky to test in humans."
What next?
DNA is now being used as a template to bioengineer nanoparticles that are able to attach to and reside in living organisms. In fact nanotechnologies have been developed that draw their energy from the body.
So it's no long shot to expect the emergence of nanotechnology implants that enable us to directly control electronics and machinery - or be controlled. Oh dear!
Things have moved on from then. Developments in nanotechnology means that data can now flow in two directions.
take the New Scientist article (reported in io9): " For the first time ever, scientists can control human brain cells using quantum dots
What if you could treat conditions ranging from Alzheimer's to blindness, all with a flash of light? Researchers think it's possible — and they plan on using tiny particles called quantum dots to do it.
Brain stimulation can be incredibly tricky. Performing it from outside the head is effective, but doesn't give you very much specificity when it comes to turning on a specific brain region...Recently, researchers have sought out solutions to these problems with methods that rely on light, in hopes that they can be used to stimulate brain activity with a high level of precision without having to crack your skull open. Right now, the buzz-word in light-mediated brain stimulation is optogenetics, which looks incredibly promising, but relies on genetic modifications that are still considered too risky to test in humans."
 |
| Nerve cells like these could be controlled by quantum dots. (Image: CNRI/Science Photo Library) |
DNA is now being used as a template to bioengineer nanoparticles that are able to attach to and reside in living organisms. In fact nanotechnologies have been developed that draw their energy from the body.
So it's no long shot to expect the emergence of nanotechnology implants that enable us to directly control electronics and machinery - or be controlled. Oh dear!
Wednesday 22 February 2012
The SoftMachine outfit's power source
(Nanowerk News) Never get stranded with a dead cell phone again. A promising new nanotechnology called Power Felt, a thermoelectric device that converts body heat into an electrical current, soon could create enough juice to make another call simply by touching it.
Developed by researchers in the Center for Nanotechnology and Molecular Materials at Wake Forest University, Power Felt is comprised of tiny carbon nanotubes locked up in flexible plastic fibers and made to feel like fabric. The technology uses temperature differences – room temperature versus body temperature, for instance – to create a charge.

Tuesday 21 February 2012
Single Atom Transistor for Quantum Computers.
A controllable transistor engineered from a single phosphorus atom has been developed by researchers at the University of New South Wales, Purdue University and the University of Melbourne. The atom, shown here in the center of an image from a computer model, sits in a channel in a silicon crystal. The atomic-sized transistor and wires might allow researchers to control gated qubits of information in future quantum computers. (Credit: Purdue University image)
Michelle Simmons, group leader and director of the ARC Centre for Quantum Computation and Communication at the University of New South Wales, says the development is less about improving current technology than building future tech. "This is a beautiful demonstration of controlling matter at the atomic scale to make a real device,"
Sunday 19 February 2012
More on Dangers of Nanoparticles in Food
Nanoparticles in Food, Vitamins Could Harm Human Health, Researchers Warn
 |
| Intestinal cell monolayer after exposure to nanoparticles, shown in green. (Credit: Image courtesy of Cornell University)caption |
According to the study, high-intensity, short-term exposure to the particles initially blocked iron absorption, whereas longer-term exposure caused intestinal cell structures to change, allowing for a compensating uptick in iron absorption.
Full article on the Science Daily link above
Friday 17 February 2012
One outfit, any colour you like, instantly.
In the Story, Alister acquires camo-dye made from quasicrystals. With controlled electrical charges, the crystals 'defect' property can be manipulated to change colour. Here's the catalyst for the idea.
From Science Daily (16 Feb, 2012) Strange New Nano-Region Can Form in Quasicrystals
"In crystals, a "defect" refers to any departure from perfect structural symmetry. While the term suggests an undesirable quality, not all defects are bad; many control or influence key material properties, such as chemical purity, mechanical strength, conductivity, color, corrosivity or surface properties.
Rubies, for instance, are red due to a defect that turns an otherwise non-descript crystal into a valuable gem."
Thursday 16 February 2012
Robugs by the millions
ScienceDaily (Feb. 15, 2012) — A new technique inspired by elegant pop-up books and origami will soon allow clones of robotic insects to be mass-produced by the sheet.
Devised by engineers at Harvard, the ingenious layering and folding process enables the rapid fabrication of not just microrobots, but a broad range of electromechanical devices.
Devised by engineers at Harvard, the ingenious layering and folding process enables the rapid fabrication of not just microrobots, but a broad range of electromechanical devices.
Make a Big note in your Diary for Black March
I'm sure you've heard from March 1st 2012 till March 31st 2012 people everywhere will be taking part in ''Black March'', this is a movement against the likes of SOPA, PIPA, and ACTA. The movement will be that, the people who take part will NOT buy magazines, books, films(movies), CDs, DVDs or even go to the Movies / Cinema, this will leave a gaping hole where it hurts the big companies; their profit margins. During ''Black March'', Anonymous will be working tirelessly, petitioning, protesting, and bringing attention to the ever growing problems of SOPA, ACTA and/or PIPA. Anonymous does not stand for censorship, and along with the rest of the internet are appalled that the American Government think it's acceptable to censor what isn't theirs.
The nanoparticles in your world, and yes, in your food too!
New research shows we are at risk of being exposed to nanoparticles in food and through domestic products far more than we realize.
Take titanium dioxide (TiO2) for example. this is a widely used additive found in food, personal care and other household products. Each year around 7 million tons of bulk TiO 2is produced annually. Why is it so popular? Well it's usedo provide whiteness and opacity to products such as paints, coatings, plastics, papers, inks, foods, pills, as well as most toothpastes. In cosmetic and personal care products, it is used as a pigment, sunscreen and a thickener.
(Source: Nanowerk News)
Perhaps the most alarming news comes from Science Daily that reports "Children may be receiving the highest exposure to nanoparticles of titanium dioxide in candy, which they eat in amounts much larger than adults, according to a new study. Published in ACS' journal, Environmental Science & Technology, it provides the first broadly based information on amounts of the nanomaterial -- a source of concern with regard to its potential health and environmental effects -- in a wide range of consumer goods."
Friends of the Earth in a recent article "Out of the Laboratory and on to our plates" report that "untested nanotechnology is being used in more than 100 food products, food packaging and contact materials currently on the shelf, without warning or FDA testing"
And as far back as Janury 2010, A House of Lords press notice: "Science and Technology Committee - Nanotechnologies and Food" begins:
LORDS SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY COMMITTEE CRITICISES THE FOOD INDUSTRY FOR FAILING TO BE TRANSPARENT ABOUT ITS RESEARCH INTO THE USES OF NANOTECHNOLOGIES
The House of Lords Science and Technology Committee today criticises the food industry for failing to be transparent about its research into the uses of nanotechnologies and nanomaterials.
In their report, Nanotechnologies and Food, the Committee notes that transparency and honesty are key components for ensuring public trust in both food safety and scientific developments, and argue that the approach of food companies in not publishing or discussing details of its research in this area is unhelpful. The Committee acknowledges that the food industry is right to be concerned about negative public reactions to developments in nanotechnologies but asserts that appearing to be secretive about its research “is exactly the type of behaviour which may bring about the public reaction it is trying to avert.”
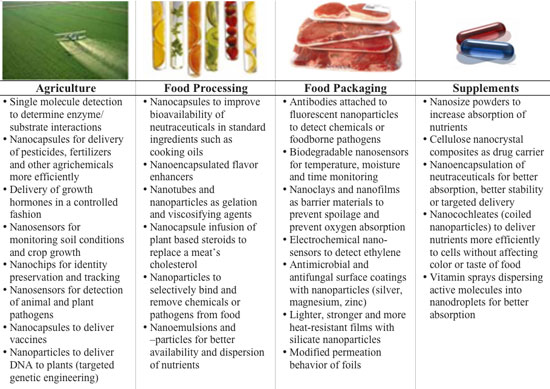
Finally from Nanowerk Spotlight, an excellent profile of some of the impact of nanotechnology in our everyday life
Wednesday 8 February 2012
Thought Control - but by whom, or what?
IBy harnessing quantum dots--tiny light-emitting semiconductor particles a few billionths of a meter across--researchers at the University of Washington (UW) have developed a new and vastly more targeted way to stimulate neurons in the brain.
Download the full PDF Here You don't have to read the whole thing (though it's well worth it if you do. But to give you a taster, and where the research might lead, the introduction begins
"Electrical signals in the brain govern the complexity of the human body and mind. Being able to switch and control these signals externally represents an important tool to answer questions about sensory, motor and behavioral events, which fundamentally control our health."
Nanowerk news (08-02-2012) reports that the University of Washington electrical engineer Lih Y. Lin and biophysicist Fred Rieke said the experiments show that "it is possible to excite neurons and other cells and control their activities remotely using light. This non-invasive method can provide flexibility in probing and controlling cells at different locations while minimizing undesirable effects."
"Many brain disorders are caused by imbalanced neural activity," Rieke adds, and so "techniques that allow manipulation of the activity of specific types of neurons could permit restoration of normal--balanced--activity levels"--including the restoration of function in retinas that have been compromised by various diseases. "The technique we describe provides an alternative tool for exciting neurons in a spatially and temporally controllable manner. This could aid both in understanding the normal activity patterns in neural circuits, by introducing perturbations and monitoring their effect, and how such manipulations could restore normal circuit activity."
Download the full PDF Here You don't have to read the whole thing (though it's well worth it if you do. But to give you a taster, and where the research might lead, the introduction begins
"Electrical signals in the brain govern the complexity of the human body and mind. Being able to switch and control these signals externally represents an important tool to answer questions about sensory, motor and behavioral events, which fundamentally control our health."
Nanowerk news (08-02-2012) reports that the University of Washington electrical engineer Lih Y. Lin and biophysicist Fred Rieke said the experiments show that "it is possible to excite neurons and other cells and control their activities remotely using light. This non-invasive method can provide flexibility in probing and controlling cells at different locations while minimizing undesirable effects."
"Many brain disorders are caused by imbalanced neural activity," Rieke adds, and so "techniques that allow manipulation of the activity of specific types of neurons could permit restoration of normal--balanced--activity levels"--including the restoration of function in retinas that have been compromised by various diseases. "The technique we describe provides an alternative tool for exciting neurons in a spatially and temporally controllable manner. This could aid both in understanding the normal activity patterns in neural circuits, by introducing perturbations and monitoring their effect, and how such manipulations could restore normal circuit activity."
Labels:
nanotechnology,
neuroscience,
quantum dots.,
Soft-Machine
Saturday 4 February 2012
Video of Action Heroes in Training,
Elizabeth Streb tells Kurt Andersen about the genesis of her "extreme choreography" on site at her dance laboratory in Brooklyn. Her new book is called, "Streb: How to Become an Extreme Action Hero." After seeing Streb's action heroes up close, Kurt learned how to start becoming one himself.
Listen to Kurt's entire conversation with Streb here:
http://www.studio360.org/episodes/2010/04/30/segments/154164
Friday 3 February 2012
Is there anybody out there? Probably yes, says scientists.
New Super-Earth Detected Within the Habitable Zone of a Nearby Cool Star
ScienceDaily (Feb. 2, 2012) — An international team of scientists led by Carnegie's Guillem Anglada-Escudé and Paul Butler has discovered a potentially habitable super-Earth orbiting a nearby star. The star is a member of a triple star system and has a different makeup than our Sun, being relatively lacking in metallic elements. This discovery demonstrates that habitable planets could form in a greater variety of environments than previously believed.Corporate Aliens. Was Alister's father right about the Centauri Foundation?
Alister's father started by joking that Aliens ran the Centauri Foundation. Later he started to believe it; to the extent that he believed they funded SETI at home in order to collect and decrypt encoded signals.
This part of my story is, like the technologies extrapolated from current developments and research, founded on real science findings and theories.
From Alpha Centauri 3
On February 25, 2008, a team of astronomers released a paper on simulation results which support the conclusions of previous studies that multiple-planet systems could have formed in close orbits around both heavy-element rich, Alpha Centauri A and B. Their simulations suggest that at least one planet in the one to two Earth-mass range could have formed within orbital distances of 0.5 to 1.5 AUs around either Star A or Star B; an important finding was that the simulations frequently generated a Earth-like planet in or near Star B's habitable zone (where liquid water could exist on the planet's surface) which can be detected with three to five years of high cadence observations (Javiera Guedes, 2009). Additional simulation work presented in the paper also indicates that long-term telescopic observations may detect wobbles from such planets using the radial velocity method. Star B, a orange-red dwarf with a relatively calm chromosphere and acoustic p-wave mode oscillations, is an easier target for detecting wobbles from terrestrial planets, possibly within only three years of "high cadence" observations for a 1.8 Earth-mass planet (more from New Scientist and Guedes et al, 2008).
Thursday 2 February 2012
Prophetic SciFi?
(Lucy Hornby and Andreas Rinke are reporting Reuters) - China is considering increasing its participation in the rescue funds aimed at resolving the European debt crisis, Chinese Premier Wen Jiabao told journalists on Thursday.
In my book, China comes to the rescue of Europe in the time of the Big Freeze.
Similarities with what's going on today it seems.
Full Reuters Article here
Followers of my blog will not have failed to notice how rapidly developments in nanotechnology, bioengineering and Neuroscience is converging and catching up with all the technologies you'll find in the first outing for Alister Cloud. Watch this space.
In my book, China comes to the rescue of Europe in the time of the Big Freeze.
Similarities with what's going on today it seems.
Full Reuters Article here
Followers of my blog will not have failed to notice how rapidly developments in nanotechnology, bioengineering and Neuroscience is converging and catching up with all the technologies you'll find in the first outing for Alister Cloud. Watch this space.
Augmented Reality Contact Lenses
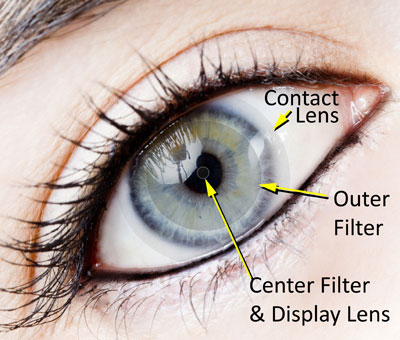
(Nanowerk News) Researchers at DARPA's Soldier Centric Imaging via Computational Cameras (SCENICC) program, based in Innovega iOptiks, are working on contact lenses that enable the wearer to view virtual and augmented reality images.
It won't be long before this, like other military innovations are commercially available and we can say bye-bye to most of our screens.
Digital images are projected onto tiny full-colour displays near the eye.
The user is able to focus both on near and far objects seamlessly giving the user the ability to continue interacting with the surrounding environment.
Anything that helps our people get a military advantage is obviously a good thing and this is a visionary edge.
Next time a solider looks at you, he'll probably know more about you than you know yourself. maybe he can tell you where you left those gig tickets.
Wednesday 1 February 2012
Don't speak. I know what your thinking
Decoding brain waves to eavesdrop on what we hear
scientists have successfully decoding electrical activity in the brain's temporal lobe as a person listens to normal conversation. Analysing the correlation between sound and brain activity, they were able to predict the words the person had heard solely from the temporal lobe activity.
"This research is based on sounds a person actually hears, but to use it for reconstructing imagined conversations, these principles would have to apply to someone's internal verbalizations," cautioned first author Brian N. Pasley, a post-doctoral researcher in the center. "There is some evidence that hearing the sound and imagining the sound activate similar areas of the brain. If you can understand the relationship well enough between the brain recordings and sound, you could either synthesize the actual sound a person is thinking, or just write out the words with a type of interface device."
scientists have successfully decoding electrical activity in the brain's temporal lobe as a person listens to normal conversation. Analysing the correlation between sound and brain activity, they were able to predict the words the person had heard solely from the temporal lobe activity.
"This research is based on sounds a person actually hears, but to use it for reconstructing imagined conversations, these principles would have to apply to someone's internal verbalizations," cautioned first author Brian N. Pasley, a post-doctoral researcher in the center. "There is some evidence that hearing the sound and imagining the sound activate similar areas of the brain. If you can understand the relationship well enough between the brain recordings and sound, you could either synthesize the actual sound a person is thinking, or just write out the words with a type of interface device."
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)















